Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty Surgical Technique
 Nov. 12, 2019
Nov. 12, 2019
Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty Surgical Technique
Operative incision
Surgical incision in flexion position of knee joint and initial exposure can reduce bleeding. The most commonly selected incision was anterior median incision, about 15cm long. The proximal end of the incision is in the middle of the femoral shaft, the middle segment is in the middle of the patella, and the distal end is close to the medial side of the tibial tubercle (Fig. 1).
Medial parapatellar approach
For primary TKA, medial parapatellar approach(Fig. 2) is the most commonly used approach. The three basic anatomical markers of the approach were: the proximal medial margin of the quadriceps femoris tendon, the midpoint of the connection between the superior medial patella and the medial femoral muscle attachment, and the inner margin of the tibial tubercle.
The proximal medial margin of quadriceps femoris tendon was preserved at 2mm and the soft tissue around the superior patella was preserved to facilitate the suture at the end of the operation. The medial soft tissue should be carefully preserved at the tubercle of the tibia and sutured to the medial edge of the patellar ligament. After joint incision, the medial and lateral edges of the patella were marked at the level of the upper pole of the patella for anatomic suture at the end of the operation (Fig. 3).
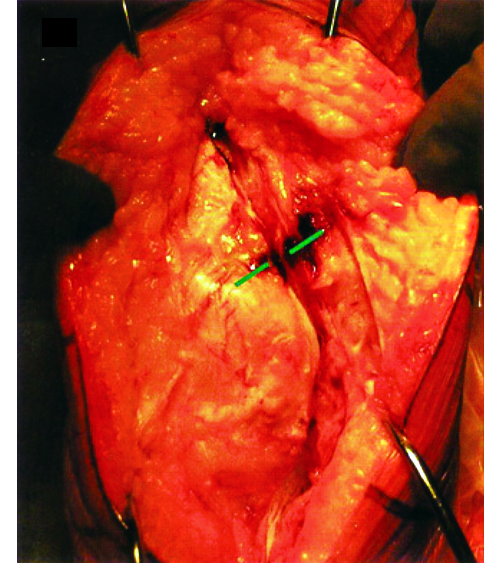
Subluxation of knee joint with external rotation of tibia, whether PCL reserved prosthesis or replacement prosthesis. External rotation relaxes the knee extension device to increase exposure and reduce the risk of patellar tendon tears.
In any operation to increase the tension of the knee joint, especially in the flexion and extension of the patella , it is important to pay attention to the attachment of the tibial tubercle of the patellar tendon. Once the patellar tendon is torn, it is difficult to repair it, which is a serious complication.













